Overview¶
Why?¶
The inspiration for MozDef comes from the large arsenal of tools available to attackers. Suites like metasploit, armitage, lair, dradis and others are readily available to help attackers coordinate, share intelligence and finely tune their attacks in real time. Defenders are usually limited to wikis, ticketing systems and manual tracking databases attached to the end of a Security Information Event Management (SIEM) system.
The Mozilla Defense Platform (MozDef) seeks to automate the security incident handling process and facilitate the real-time activities of incident handlers.
Goals¶
High level¶
- Provide a platform for use by defenders to rapidly discover and respond to security incidents.
- Automate interfaces to other systems like MIG, flowspec, load balancers, etc
- Provide metrics for security events and incidents
- Facilitate real-time collaboration amongst incident handlers
- Facilitate repeatable, predictable processes for incident handling
- Go beyond traditional SIEM systems in automating incident handling, information sharing, workflow, metrics and response automation
Technical¶
- Replace a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Scalable, should be able to handle thousands of events per second, provide fast searching, alerting, correlation and handle interactions between teams of incident handlers.
MozDef aims to provide traditional SIEM functionality including:
- Accepting events/logs from a variety of systems
- Storing events/logs
- Facilitating searches
- Facilitating alerting
- Facilitating log management (archiving,restoration)
It is non-traditional in that it:
- Accepts only JSON input
- Provides you open access to your data
- Integrates with a variety of log shippers including heka, logstash, beaver, nxlog and any shipper that can send JSON to either rabbit-mq or an HTTP endpoint.
- Provides easy python plugins to manipulate your data in transit
- Provides realtime access to teams of incident responders to allow each other to see their work simultaneously
Architecture¶
MozDef is based on open source technologies including:
- Nginx (http(s)-based log input)
- RabbitMQ (message queue and amqp(s)-based log input)
- uWSGI (supervisory control of python-based workers)
- bottle.py (simple python interface for web request handling)
- elasticsearch (scalable indexing and searching of JSON documents)
- Meteor (responsive framework for Node.js enabling real-time data sharing)
- MongoDB (scalable data store, tightly integrated to Meteor)
- VERIS from verizon (open source taxonomy of security incident categorizations)
- d3 (javascript library for data driven documents)
- dc.js (javascript wrapper for d3 providing common charts, graphs)
- three.js (javascript library for 3d visualizations)
- Firefox (a snappy little web browser)
Frontend processing¶
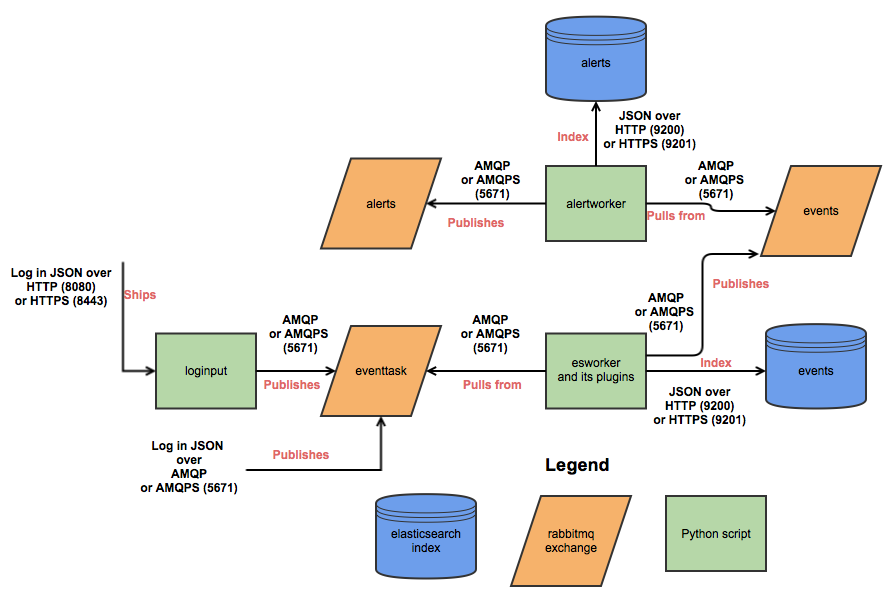
Frontend processing for MozDef consists of receiving an event/log (in json) over HTTP(S) or AMQP(S), doing data transformation including normalization, adding metadata, etc. and pushing the data to elasticsearch.
Internally MozDef uses RabbitMQ to queue events that are still to be processed. The diagram below shows the interactions between the python scripts (controlled by uWSGI), the RabbitMQ exchanges and elasticsearch indices.
Status¶
MozDef is in production at Mozilla where we are using it to process over 300 million events per day.
Roadmap¶
Initial Release:
- Facilitate replacing base SIEM functionality including log input, event management, search, alerts, basic correlations
- Enhance the incident workflow UI to enable realtime collaboration
- Enable basic plug-ins to the event input stream for meta data, additional parsing, categorization and basic machine learning
- Support as many common event/log shippers as possible with repeatable recipies
- 3D visualizations of threat actors
Mid term:
- Repeatable installation guides
- Ready-made AMIs/downloadable ISOs
- Correlation through machine learning, AI
- Base integration into Mozilla’s defense mechanisms for automation
- Fine tuning of interactions between meteor, mongo, dc.js
- Support a variety of authentication/authorization schemes/technologies
- Plain text version of attackers
- Enhanced search for alerts, events, attackers within the MozDef UI
Long term:
- Integration into common defense mechanisms used outside Mozilla
- Enhanced visualizations and interactions including alternative interfaces (myo, omnidirectional treadmills, oculus rift)